By Lucero Artemio, Senior Product Manager, Fiberroad Technology
There are several key advantages of power over Ethernet (PoE) technology. This technology is also suitable for wide-spread networks. It is a good way to understand what this technology is all about. Here are some of the advantages of power over Ethernet:
Low cost
PoE can save your business time and money by integrating power into your IP network. The new technology can reduce installation times and minimize the need for additional wiring. It is also more secure and convenient than standard AC power connections. With PoE, you can place your devices anywhere they need to be without worrying about whether they have enough power. It can also reduce the cost of building and maintaining electrical power cables.
When you use Power over Ethernet, you can avoid the cost and complexity of installing separate connections for each endpoint. Moreover, Power over Ethernet can take advantage of your existing LAN infrastructure to support IP endpoints. By using PoE, you can use the same cables for both data and power. It also helps reduce network complexity and costs. This technology is suitable for small, medium, and large businesses. This technology is easy to integrate with existing network infrastructure and can be deployed with minimal effort.
Power over Ethernet is a great solution for organizations that need to extend their network reach. PoE is becoming an increasingly popular way to connect office locations. Power over Ethernet can also help businesses save money by enabling more remote locations to connect to the network. Low-cost PSEs are the cheapest and most flexible solution to connect your office to the rest of the world. The benefits of this technology are endless. With its flexible and efficient setup, PoE has the potential to improve your business’ productivity and profitability.
Easy to implement
Using Power over Ethernet can be an excellent way to save money and time while installing and running a business IP network. This technology can help make your home or office more flexible and convenient by adding an additional power source without the hassle of complicated electrical installations.
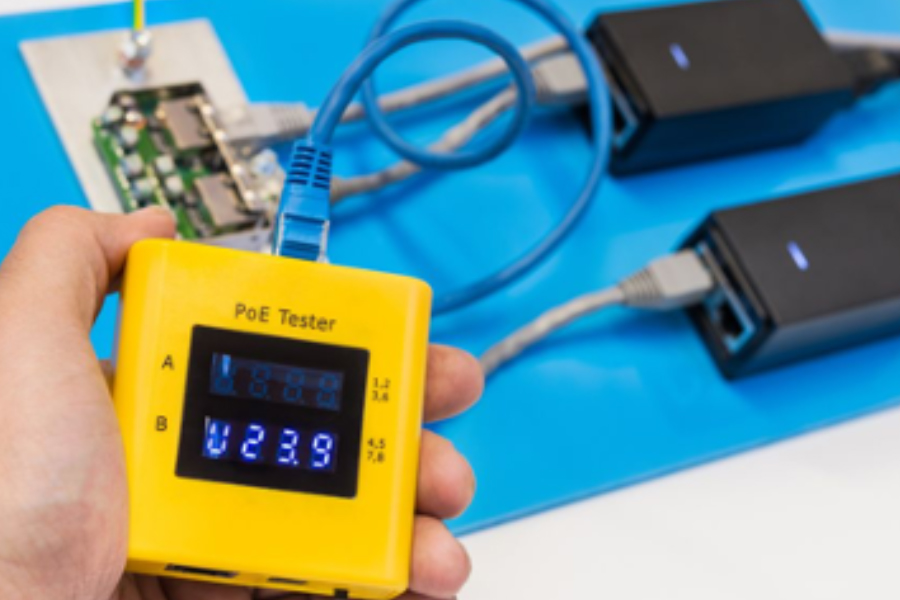
Power over Ethernet is a technology that allows you to pass electrical power and data over a single Ethernet cable. It works by connecting devices with a PoE capability to a network via an Ethernet cable. Power over Ethernet technology allows for the transfer of power and data through Ethernet data cables. This technique is ideal for smart homes and business premises because it allows you to use less expensive Ethernet cabling. Besides saving money, PoE allows you to preserve your existing electrical wiring.
Reliability
Reliability is critical for power over Ethernet systems. Unlike AC power, which can cause crosstalk, power over Ethernet systems require higher frequency to send current. This also limits the power capacity of the system and increases the inductance. Some disadvantages of power over Ethernet include potential for network disruption and interference with data signal transmission. It also requires power conditioning and is subject to liability for any problems with the power supply in the connected equipment.
Reliability of power over Ethernet is critical for voice over IP, wireless, and servers. It is important to find a solution that is optimized for power requirements at the source. This will include filtering, testing, and isolation of problems. In addition, a reliable power supply will eliminate the possibility of failure. This way, the data center can stay up and running. In addition, it will help reduce the need to upgrade the data center.
Widely distributed network
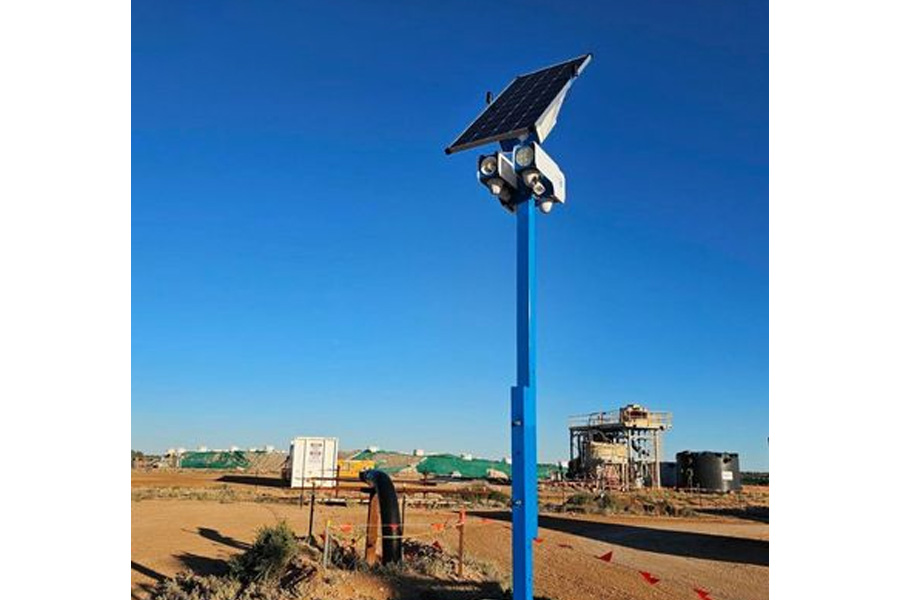
One of the key benefits of power over Ethernet is that it is easily deployed at remote sites, which means less need for electrical installations and reduced cost of employing electrical contractors. To install PoE devices, you’ll need a combination of networking and power sourcing equipment. In many cases, you’ll need twisted-pair cable, Cat 3 or 5 cabling, and coaxial cable. This method can be installed almost anywhere, which allows network administrators to reduce their costs and simplify deployment.
PoE is a low-voltage technology for delivering DC power and data over a single Ethernet cable. As the number of connected devices increases, power consumption can quickly mount a significant burden on traditional compute/storage models. Power over Ethernet has been well adapted to widely distributed networks, including campuses and smart cities. By combining power and data in a single cable, PoE can support more sustainable outcomes and reduce the need for power-consuming cabling.
Power over Ethernet is a powerful solution for businesses that need to update their systems frequently. By using the capabilities of a network cable to transmit power, PoE enables businesses to power their devices without having to add additional power outlets. In addition to its advantages for updating systems, PoE can also be used to power a variety of devices. It’s easy to install and enables an easy upgrade process. And unlike traditional wiring, PoE is not limited to data.
Scalability
Power over Ethernet deployments are fast and easy, particularly when leveraged with existing network infrastructure. In the simplest case, deployments require the installation of a PoE switch in an MDF closet and connecting the cabling to the network. Depending on the needs of the organization, PoE deployments may be physically separate from the core network or centrally converged. Either way, Power over Ethernet increases network performance and security while enabling users to take advantage of the benefits of thin clients.
Fiberroad invented POE in 2000 as a proprietary technology that enables scalable power delivery for IP-telephony handsets. It works by emulating a land-line PSTN phone by sending 48V DC power through the same copper cabling used for communications. Initially, the technology took advantage of unused pairs of Cat 5 cable wires. Today, PoE is a widely-used method of delivering power to IP-telephony devices